May Is Skin Cancer Awareness Month

Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the U.S. One in five Americans will develop skin cancer by age 70. Unprotected sun exposure over the years has left many people vulnerable. Many of these are affected by actinic keratosis, the most common precancer.
Skin cancer is one of the most preventable cancers. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher helps protect skin from harmful UVA and UVB light rays. Reapply sunscreen as directed, especially after sweating or swimming. Stay out of the sun during peak hours of intensity. Cover up with clothing, a hat, and sunglasses. Avoid tanning beds. Indoor tanning increases the risk for skin cancer.
The three most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. The American Cancer Society recommends people ages 20-40 have a professional skin cancer exam every three years, particularly if they live in sunny climates. People over age 40 should have a skin cancer screening annually.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
This is the most common type of skin cancer. It may look like a flesh-colored, pearl-like bump or a patch of pinkish skin. It can form anywhere on the body but is common on the head, neck, and arms. People with fair skin are particularly vulnerable.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The second most common type of skin cancer is squamous cell carcinoma. People with lighter skin are most likely to develop it. The cancer can look like a scaly patch, a red bump, or a sore that doesn’t heal. It is commonly seen on the face, ears, neck, arms, back, and chest.
Melanoma
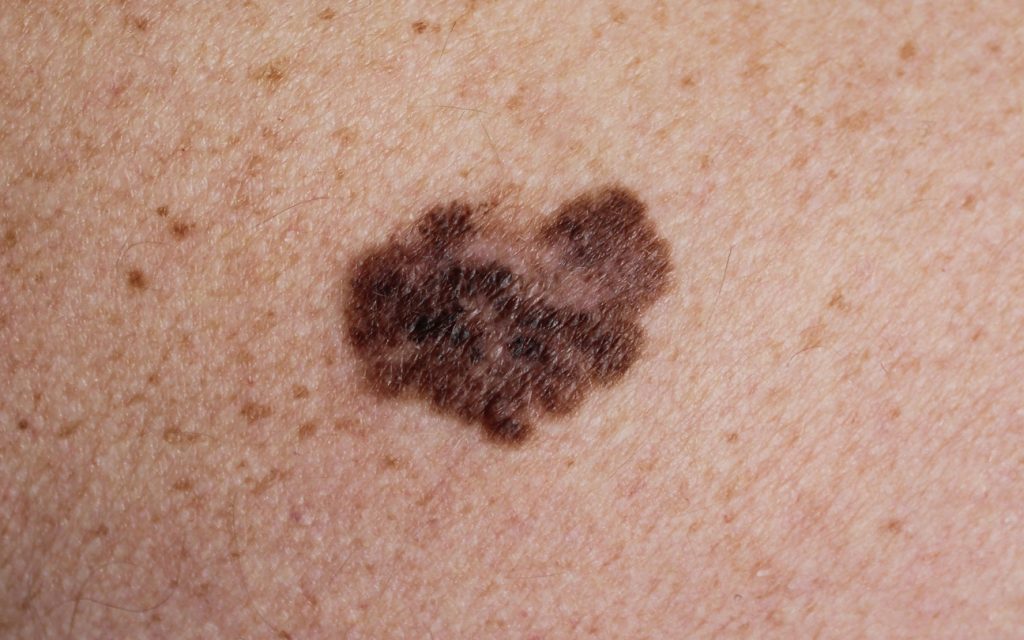
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer because of its tendency to spread. It can develop in a mole or appear as a new dark spot. The spot will look asymmetrical and have irregular borders. Existing moles that change in shape, size, color, or feel should be examined by a physician. Melanoma commonly is seen on the legs of women and on the chest and back of men. Early diagnosis is crucial for successful treatment.
Next Steps
The physicians at RMD Primary Care can perform surgical biopsies of suspicious skin cancer lesions or moles. There is minimal discomfort to the patient as the site is numbed first. The specimen will be sent to a lab for analysis and testing. If skin cancer is diagnosed, we can refer patients to a specialist. Contact us for an evaluation appointment if you have any areas of concern.




